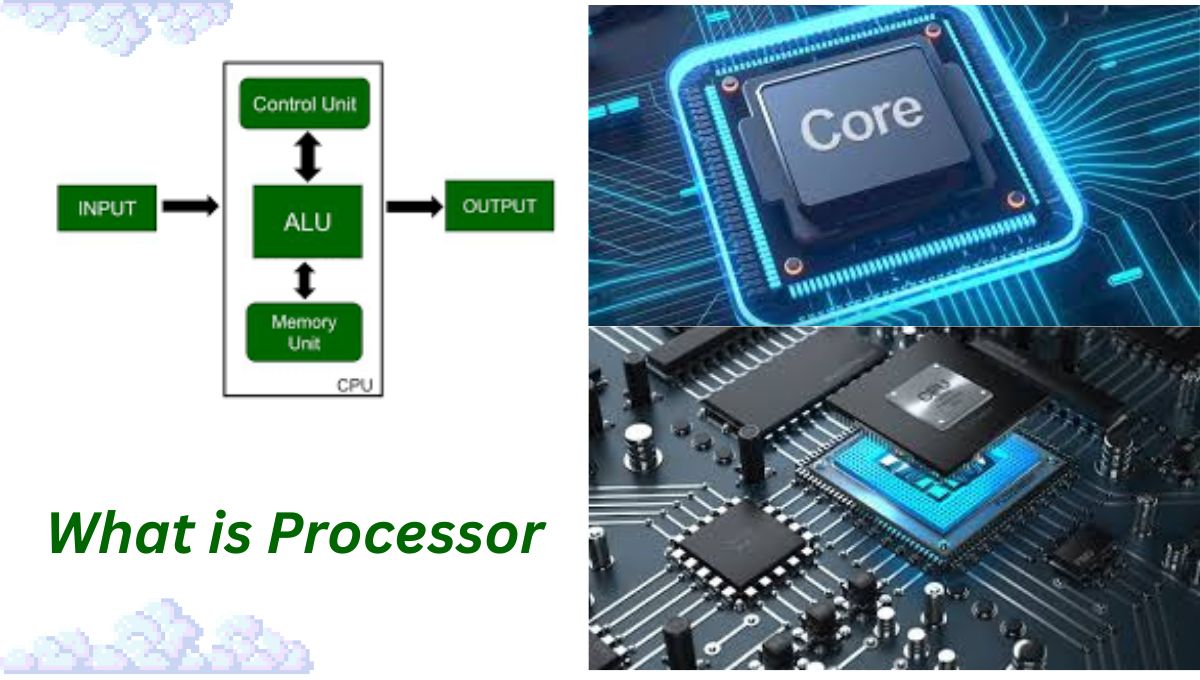
What is Processor:A processor , also known as the Central Processing Unit (CPU) ,
is the primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing inside
a computer. It executes instructions from programs and processes data by performing
basic arithmetic, logic, control, and input / output operations specified by the instructions
in the program. The CPU is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, responsible for
interpreting and executing commands from both hardware and software.
Key Functions of a Processor
Instruction Execution: The processor executes instruction from programs stored in the computers memory. These instructions are executed in a cycle: fetch , decode and execute.
- Fetch: The processor retrieves an instruction from memory.
- Decode: The processor interprets the instruction.
- Execute: The processor performs the operation specified by the instruction.
- Store: The results of the operation are written back to memory or a register.
Arithmetic and Logic Operations: The processor performs basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It also performs logic operation like AND , OR, NOT and XOR.
Control Operations: The processors controls the sequence of operations by managing the flow of data within the computer system and coordinating the activities of other hardware components.
Input/Output Operations: The processor manages data transfer to and from peripheral devices, such as keyboards, mice, displays and storage devices.
Components of a processor
Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU): The part of that performs arithmetic and logic operations. It is responsible for carrying out mathematical calculations and logical comparisons.
Control Unit (CU): The part of that directs the operation of the processor by fetching instructions from memory, decoding them and executing them. It also manages the flow of data between the CPU and other components of the computer.
Registers: Small, fast storage locations within the processor that temporarily hold data and instructions. They provide quick access to data that the CPU needs to process.
Cache Memory: A small , fast memory located close to the core that stores frequently accessed data and instructions to speed up processing. It helps to speed up processing by reducing the time it takes to access data from the main memory (RAM).
Types of Processors
Single-core Processors: Processors with a single processing unit or core. These are less common today but were widely used in early computers but have been largely replaced by multi-core processors in modern systems.
Multi-Core Processors: Processors with multiple processing units or cores. Each core can execute instruction independently , allowing for more efficient multitasking and parallel processing. Examples includes dual-core, quad-core and octa-core processors.
Importance of a Processor
The r is a crucial for the overall performance and functionality of a computer system. It determines how quickly and efficiently a computer can execute tasks, run applications and process data. Advances in processor technology, such as increased clock speeds, more cores and improved architectures, have significantly enhanced the capabilities of modern computers.
Conclusion
IN summary, the heart of any computer system , enabling it to perform a wide range of tasks by executing instructions, processing data and managing hardware resources.